Proof of value (POV) process
Moderne automates code maintenance tasks like framework migrations, security vulnerability fixes, and code quality improvements. Work that traditionally takes months can be completed in minutes, freeing developers to focus on delivering business value.
This guide walks through a typical proof of value (POV) process to help you evaluate Moderne's capabilities. We recommend starting with lower-risk tasks like code quality improvements before moving to more complex migrations.

Proof of value steps
- Moderne Platform
- Moderne CLI
-
Platform provisioning - Moderne provisions an isolated platform in your chosen cloud provider and region (takes ~1 hour).
-
Mass Ingest - Your team sets up an ingestion pipeline to build and publish LST artifacts for your repositories. You should start with 100 or more diverse repositories for best results. This step does not require you to make any changes to the repositories themselves (such as installing build plugins).
-
Agent setup - Your team sets up the Moderne agent following our on-premise agent configuration doc. The agent runs as a Docker image or JAR and connects to your source code manager (SCM) and artifact repository using read-only service accounts (takes less than 1 hour with accounts ready).
-
Run recipes - With everything set up, you can now run recipes against your code. We strongly recommend starting with simple code quality improvement recipes before progressing to complex migrations. You can find our recommended recipes to run and examples of what they do in the next section of this doc.
-
Study results - After you've run a recipe, you should generate data tables and visualizations to learn more about what happened.
The recipes below progress from simple to complex. Links go to the public Moderne Platform where you can test on open-source repositories. You can also run these recipes using the CLI commands provided in each section.
-
Download the Moderne CLI – Download the latest JAR from Maven Central.
- While not required, you are strongly encouraged to set up an alias for running the JAR.
- Note: You may experience a few speed bumps related to your internal nexus/scanners that block recipes JARs. For example, the Spring migrations recipes have migrations going back a few major versions. Those versions call out now vulnerable dependencies – but those calls may get blocked by your firewall as it doesn't recognize what the purpose of the recipe is. Ideally this is not an issue, but if it is, please let us know, and we'll work together with you to address it.
-
Clone repos to your local machine – In order for the CLI to run recipes against your code, you will need to provide it with a repos.csv file.
- Once you've created the
repos.csvfile, create a directory somewhere on your machine and run the following command:mod git sync csv . repos.csv
- Once you've created the
-
Build LSTs for the repos you cloned – With all of the repositories cloned to your machine, you'll need to build the LSTs for them by running the following command:
mod build .-
Note: All of your LSTs may not build successfully. This is a normal experience during initial ingestion as there are always unique configurations and environmental factors that need to be accounted for. We can work with you to investigate these issues on a call.
- The CLI stack trace will give some hints as to the issue. There is also a
build.logfile produced to every repo that will contain more context. You can also run the following command to aggregate the build logs:
mod log builds add . logs.zip --last-build- Common reasons LSTs may fail to build:
- Using Java versions older than Java 8
- Partially checked-in or outdated wrapper files that are not used in CI
- Builds that depend on system properties or environment variables that are set locally or in CI but not documented
- Using Gradle versions older than 4.10
- Non-standard locations for Maven's
settings.xmlor local repository - Unusual Maven profile activation conditions
- The CLI stack trace will give some hints as to the issue. There is also a
-
-
Add your CLI key – By now, you should have received a CLI key for the purposes of this PoC. Run the following command to add the key, which will allow you to download and run recipes:
mod config license edit <insert provided key here> -
Install the recipes – Copy and run the Moderne CLI command under CLI installation.
-
Try your first recipe – Try a simple recipe to test that you can execute successfully against the LSTs you built in step 3. We recommend the "Find empty classes" recipe, which will search through your repos to find empty classes that do not implement an interface or extend a class. To run this recipe, run the following command:
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.search.FindEmptyClasses
Code quality recipes
Common static analysis issues
Resolves common static analysis issues (SAST issues) to improve code quality, fix mistakes, eliminate legacy patterns, and resolve performance issues.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.staticanalysis.CommonStaticAnalysis
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
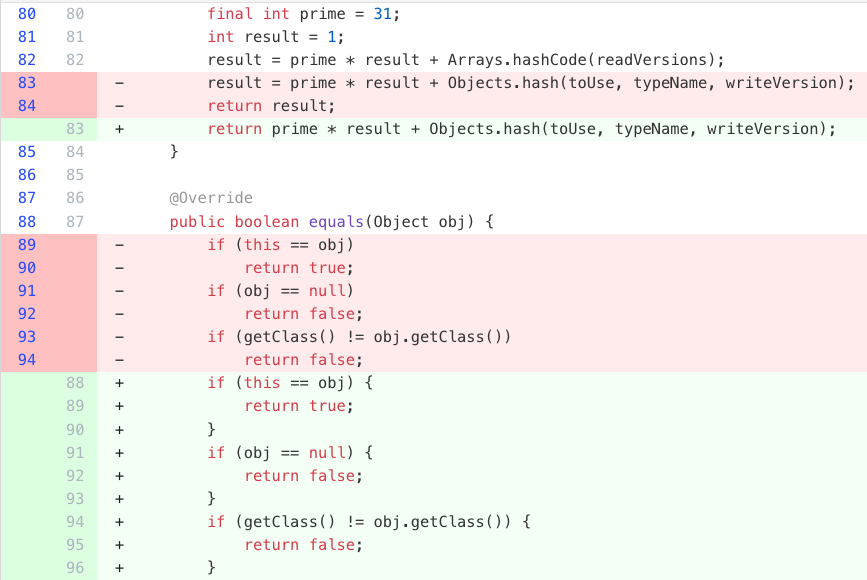
Logging improvements
Parameterize SLF4J logging statements
Converts string concatenation in log statements to parameterized logging for significant performance boosts, especially when log levels are disabled.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.logging.slf4j.ParameterizedLogging
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
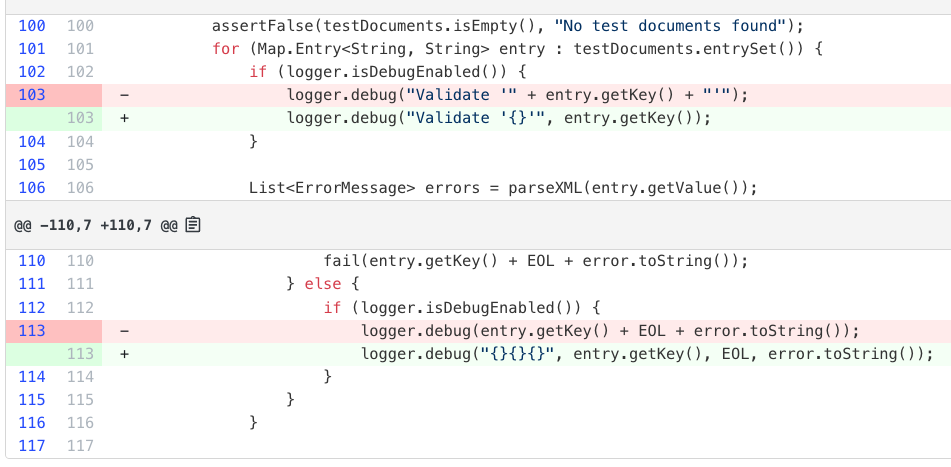
Complete exception logging
Ensures exceptions are logged with full stack traces rather than just messages. Many exception types lack useful messages, and stack traces are critical for debugging.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.logging.slf4j.CompleteExceptionLogging
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
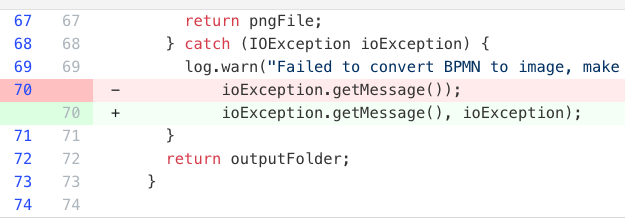
Dependency management
Dependency insight for Gradle and Maven
Finds all dependencies (including transitive) across Gradle and Maven projects. Useful for identifying version inconsistencies that can cause runtime issues.
CLI commands
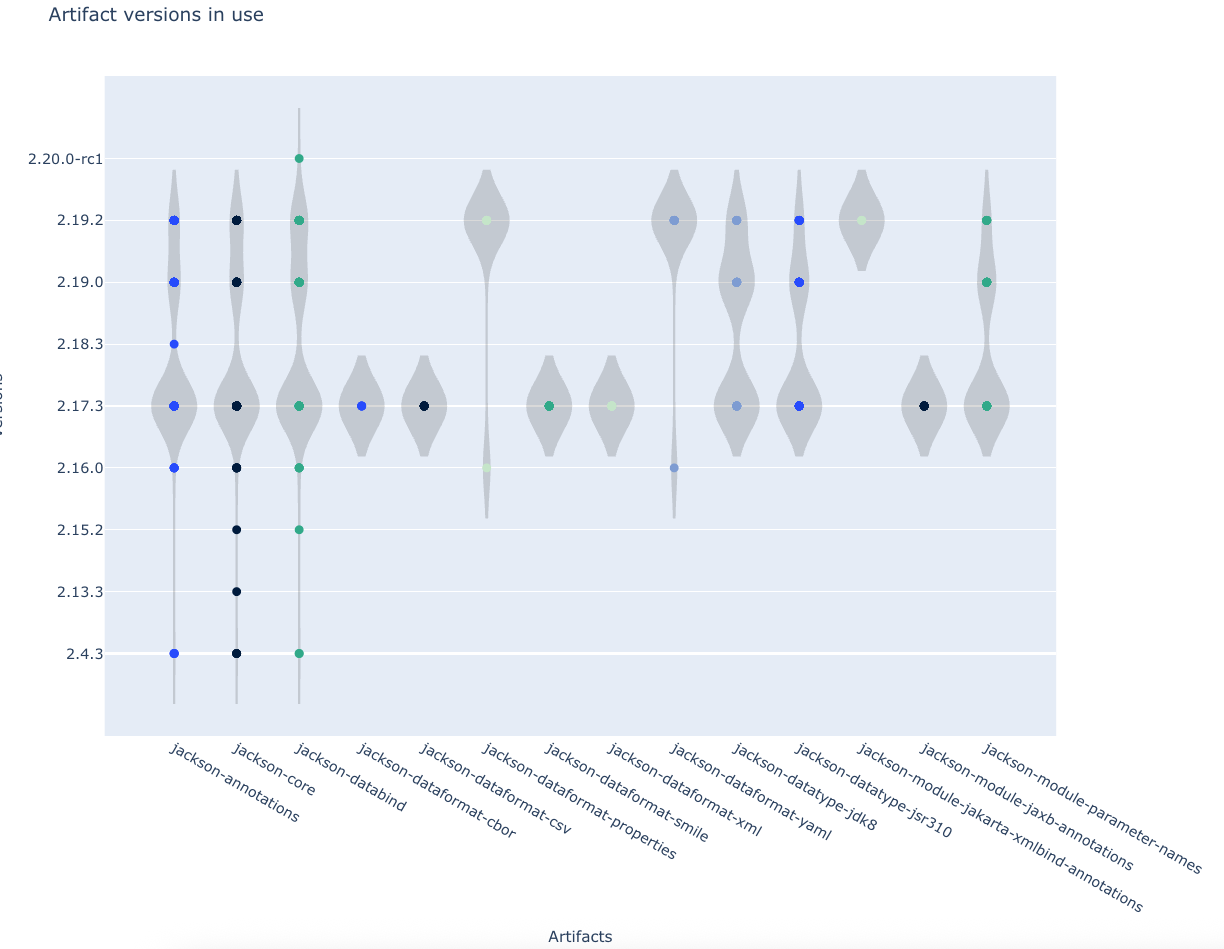
# Example: Find all Jackson library versions
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.dependencies.DependencyInsight \
-P "groupIdPattern=com.fasterxml.jackson.*" \
-P "artifactIdPattern=*" \
-P "scope=runtime"
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table DependenciesInUse
Recipe results
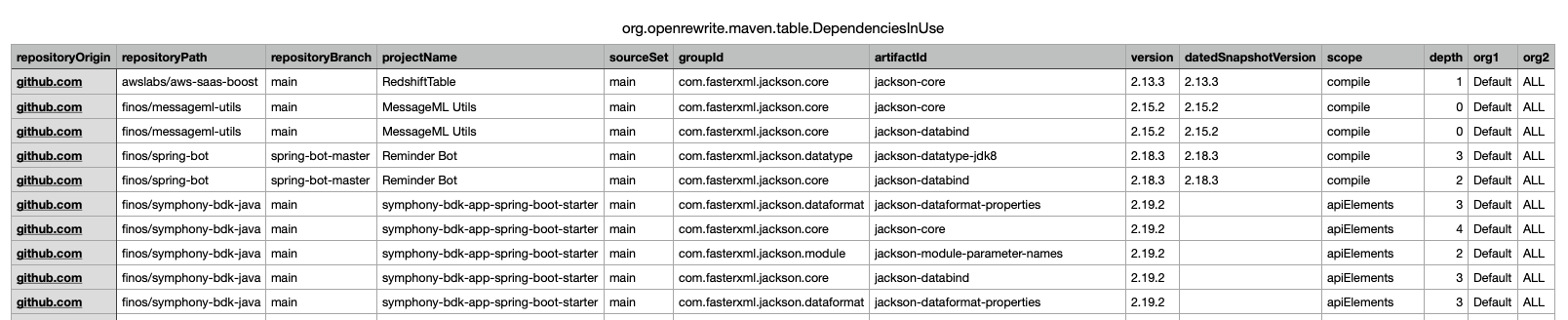
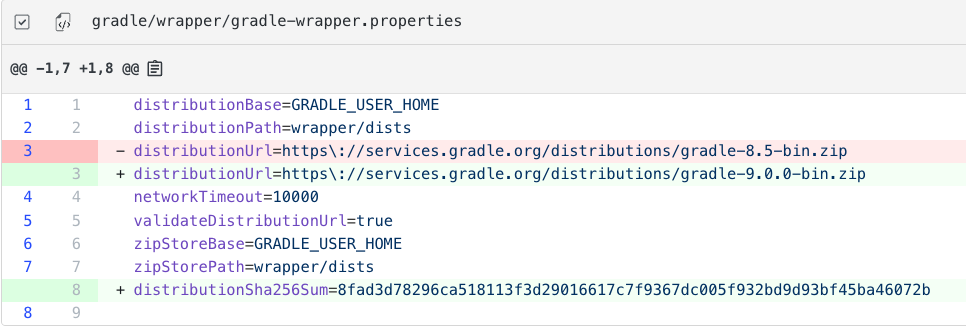
Update Gradle wrapper
Updates Gradle wrapper to the latest version, querying
services.gradle.orgfor available releases while respecting your artifact repository configuration.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.gradle.UpdateGradleWrapper
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
Update Gradle plugins
Updates Gradle plugins by ID to newer versions.
CLI commands
# Update specific plugin - adjust parameters for your plugins
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.gradle.plugins.UpgradePluginVersion \
--recipe-option "pluginIdPattern=org.springframework.boot" \
--recipe-option "newVersion=3.4.x"
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
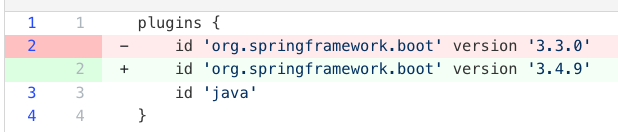
build.gradle change.Security
Find secrets
Locates secrets like passwords, API keys, and tokens stored in plain text.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.security.secrets.FindSecrets
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
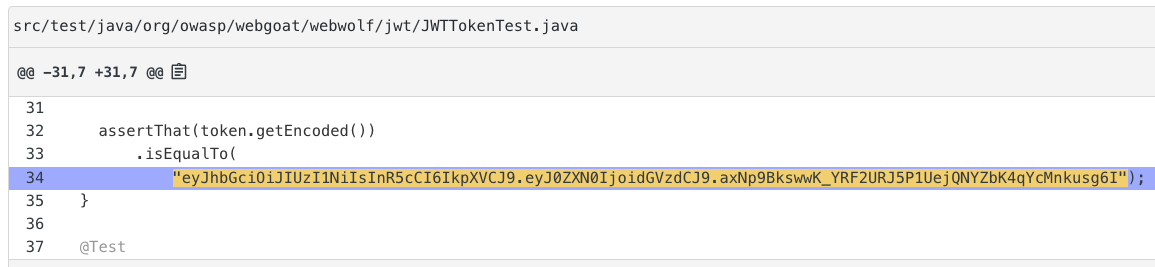
Use secure random
Replaces
java.util.Randomwith cryptographically securejava.security.SecureRandom.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.security.SecureRandom
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
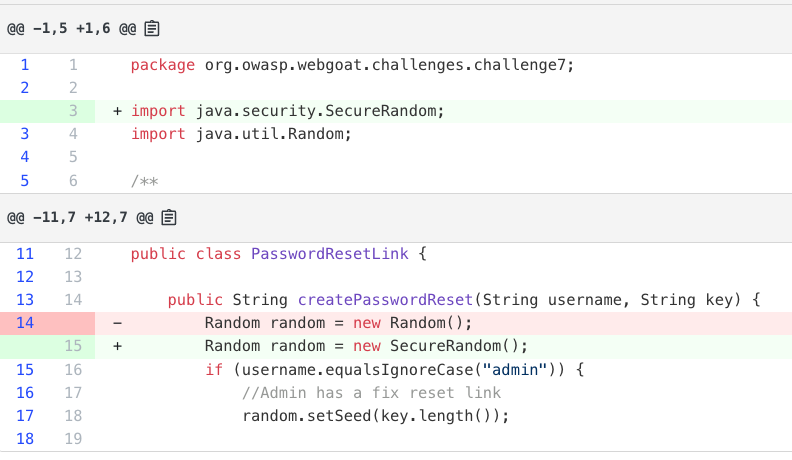
Random being replaced with SecureRandom.Java security best practices
Applies multiple security improvements including XML parser XXE vulnerability fixes, secure temporary file creation, Zip slip vulnerability remediation, file descriptor leak prevention, and loop condition safety checks.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.security.JavaSecurityBestPractices
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
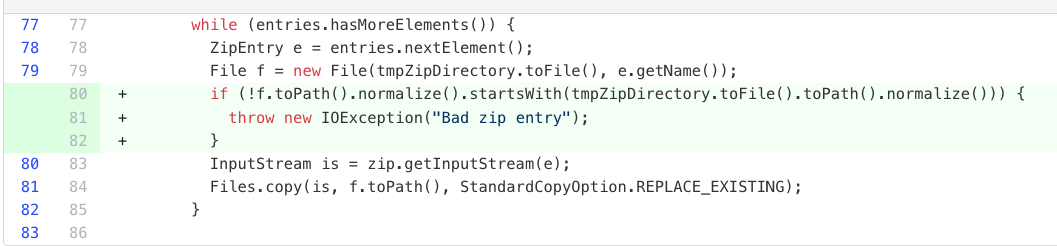
OWASP Top Ten
Identifies and remediates vulnerabilities from the OWASP Top Ten including broken access control, cryptographic failures, injection, security misconfiguration, vulnerable components, and data integrity failures.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.security.OwaspTopTen
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
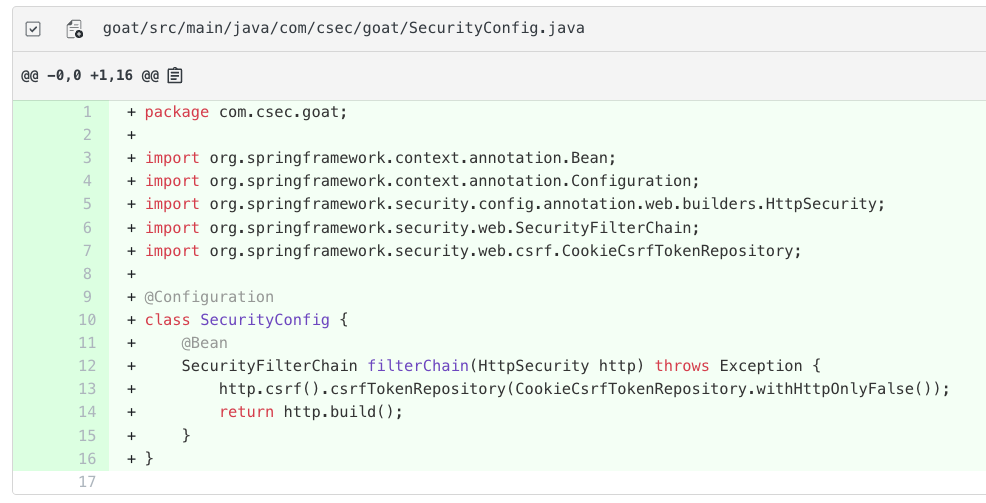
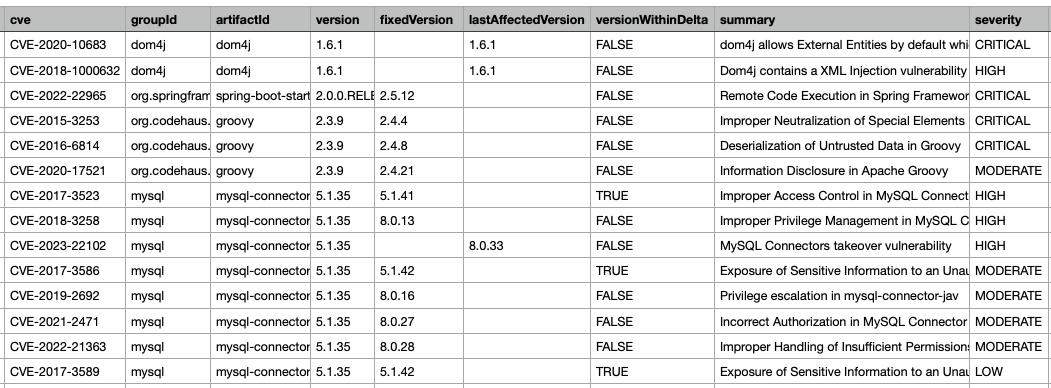
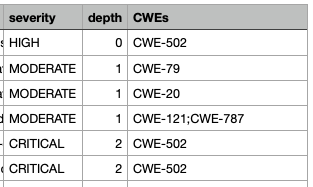
Find and fix vulnerable dependencies
Software composition analysis (SCA) tool that detects and upgrades dependencies with known CVEs. Uses GitHub Security Advisory Database which aggregates multiple vulnerability databases including the National Vulnerability Database.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.dependencies.DependencyVulnerabilityCheck \
-P "scope=runtime" \
-P "overrideTransitive=True" \
-P "maximumUpgradeDelta=patch"
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table VulnerabilityReport
Recipe results
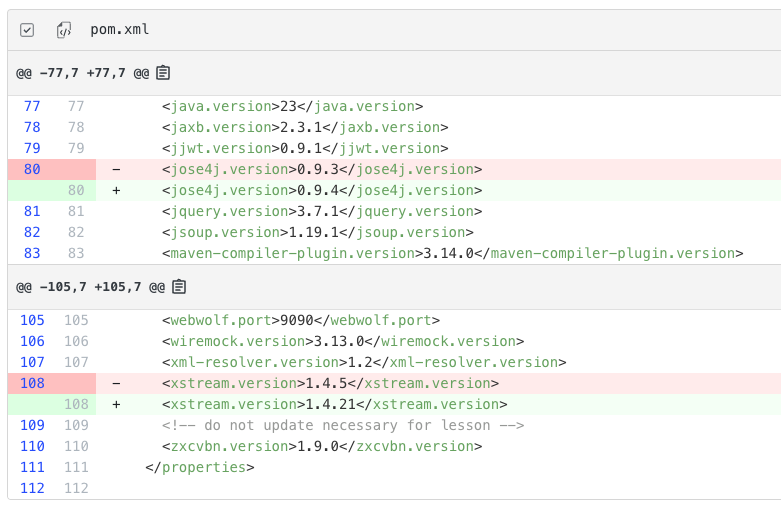


Test modernization
JUnit Jupiter best practices
Migrates to JUnit 5 and applies best practices to tests. This recipe will: migrate from JUnit 4.x to JUnit Jupiter, statically import JUnit Jupiter assertions, remove the test prefix and public visibility from JUnit 5 tests, add
@ParameterizedTestannotations, and improve lifecycle methods – among other things.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.testing.junit5.JUnit5BestPractices
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
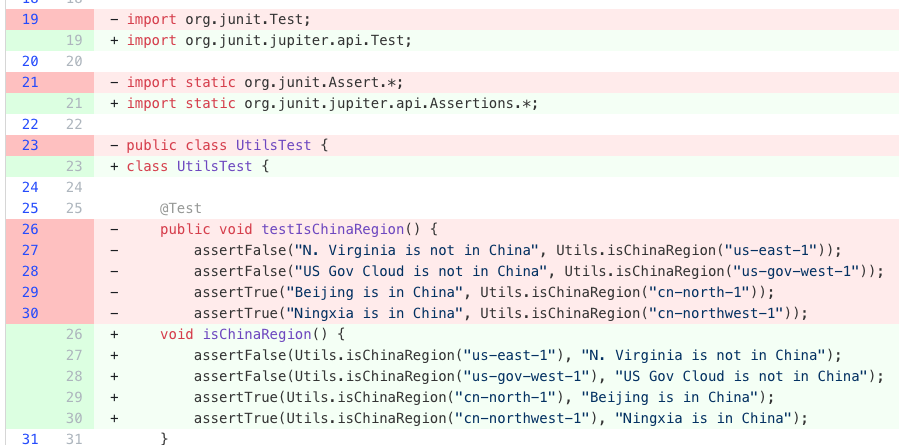
AssertJ best practices
Migrates assertions to AssertJ for better readability. Migrates from JUnit, Hamcrest, Fest, and TestNG assertions, statically imports
assertThat, simplifies chained assertions, and adopts type-specific assertions.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.testing.assertj.Assertj
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
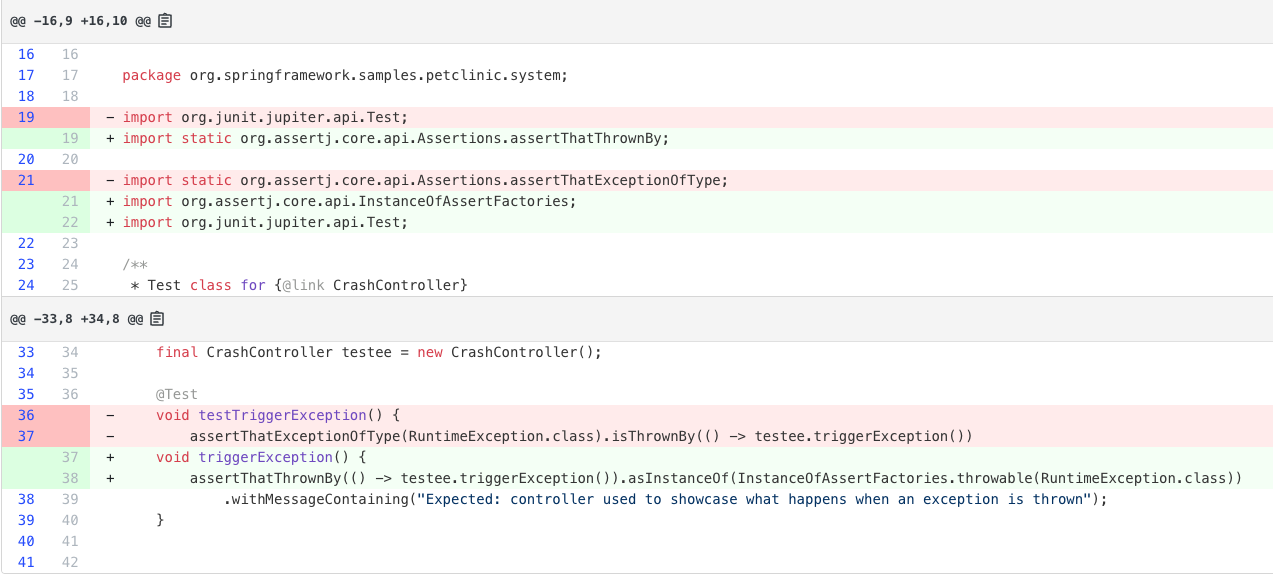
Major migrations
Major migrations are complex transformations that typically automate 80-90% of the work, with the remainder requiring manual developer intervention. They are typically composed of multiple, complex recipes.
Migrate to Java 21
Comprehensive migration from Java 8/11 to Java 21. Updates build files for Java 21 target/source, replaces deprecated APIs, adopts new language features, upgrades plugins to Java 21 compatible versions, and updates GitHub Actions configurations.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe org.openrewrite.java.migrate.UpgradeToJava21
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results


Spring Boot 3.5 best practices
Migrates to Spring Boot 3.5 and applies best practices. Includes upgrades from prior Spring Boot versions with configuration updates and dependency alignment.
CLI commands
mod run . --recipe io.moderne.java.spring.boot3.SpringBoot3BestPractices
mod study . --last-recipe-run --data-table SourcesFileResults
Recipe results
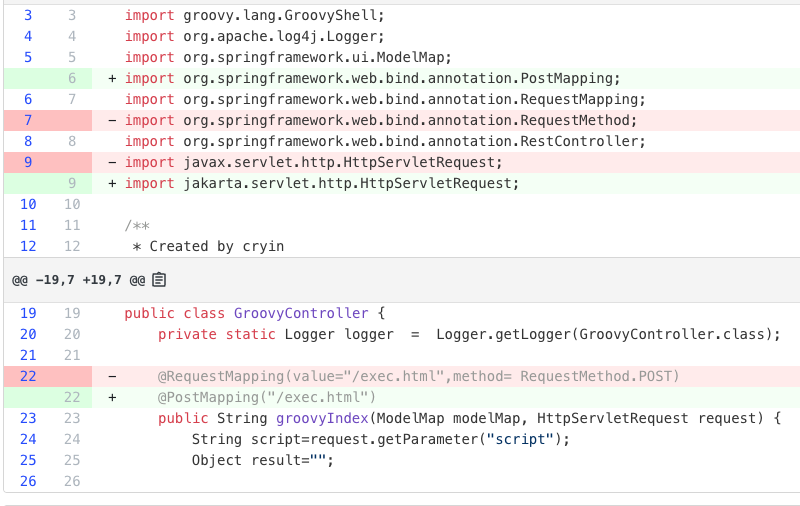
Impact analysis
Impact analysis helps you understand the consequences of changes before making them. Use these recipes to identify what will be affected: